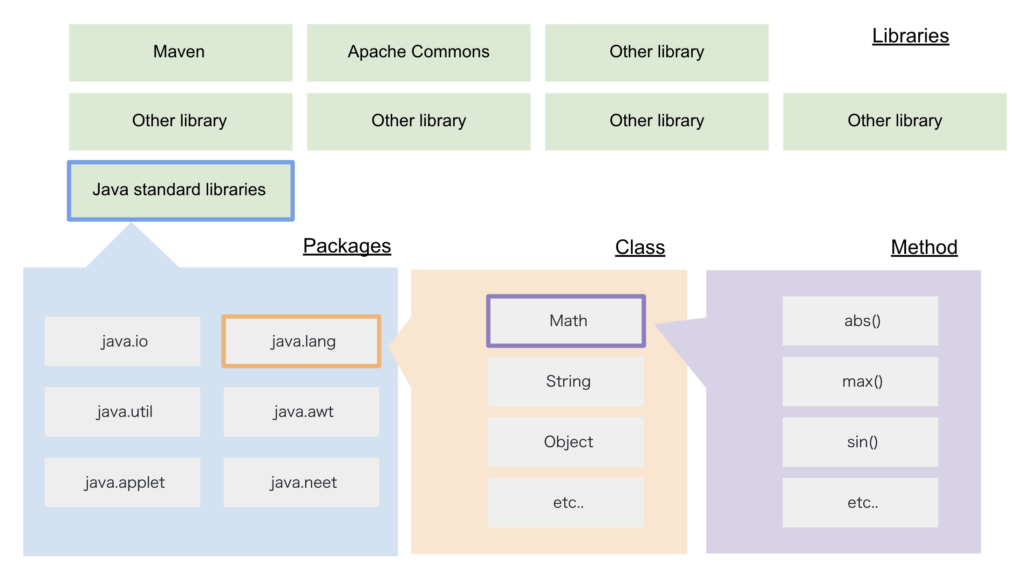
When Method is written using return in Java, data_type should be matched in 〇〇 area as below:
public static 〇〇 method_name(arguments) {
}When return value is int
Method should be written as 「public sttatic int method_name()」
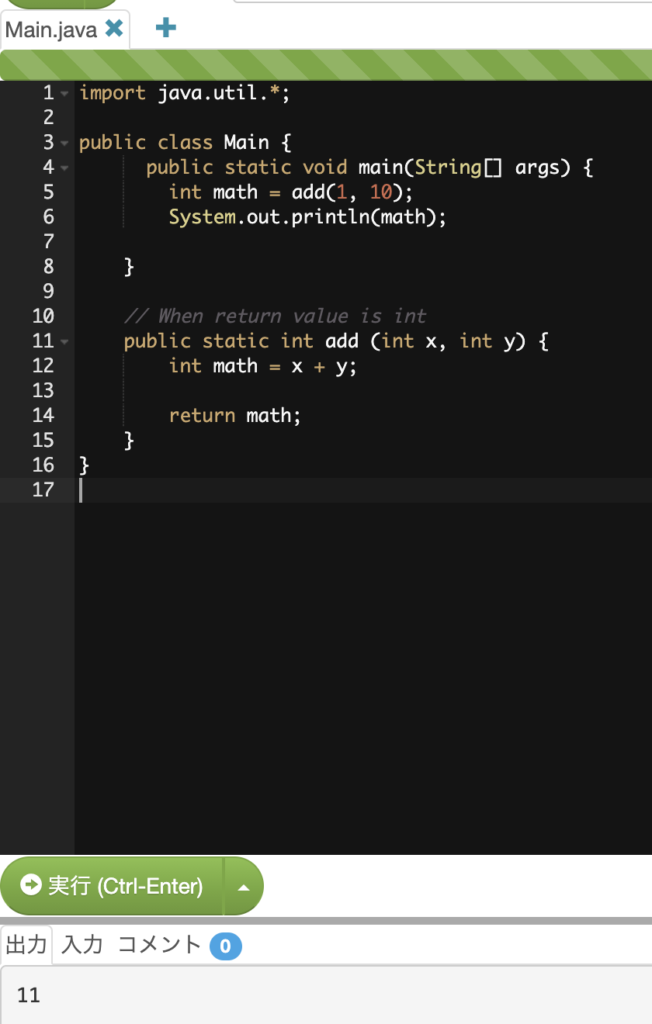
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int math = add(1, 10);
System.out.println(math);
}
// When return value is int
public static int add (int x, int y) {
int math = x + y;
return math;
}
}
When return value is String
Method should be written as 「public static String method_name()」
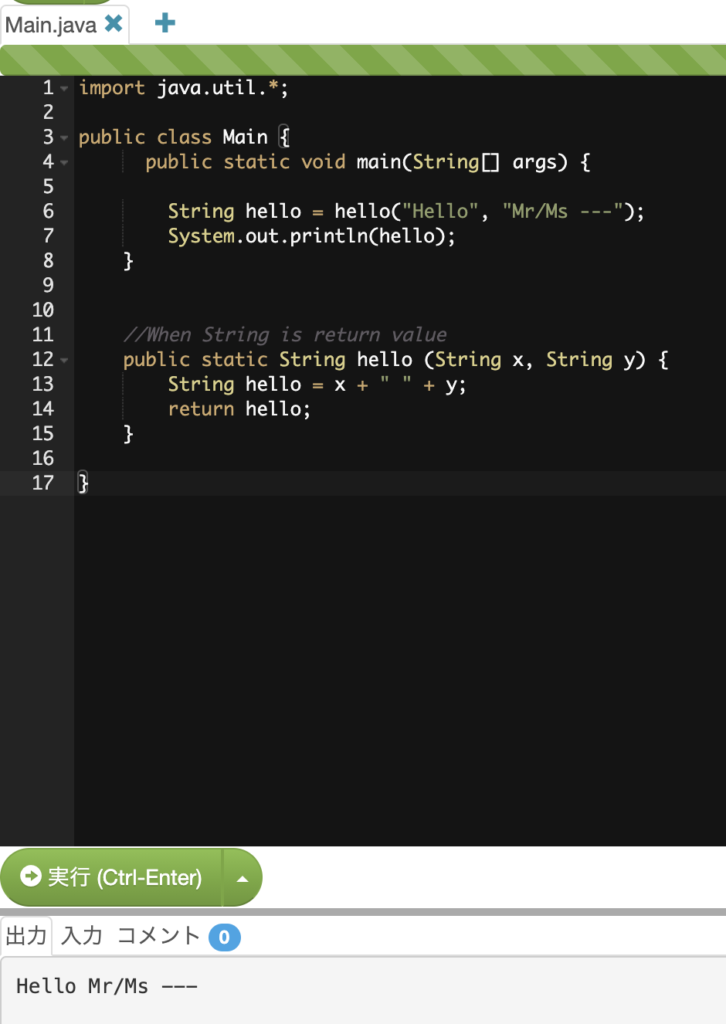
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hello = hello("Hello", "Mr/Ms ---");
System.out.println(hello);
}
//When String is return value
public static String hello (String x, String y) {
String hello = x + " " + y;
return hello;
}
}When return value is boolean
Method should be written as 「public static boolean method_name()」
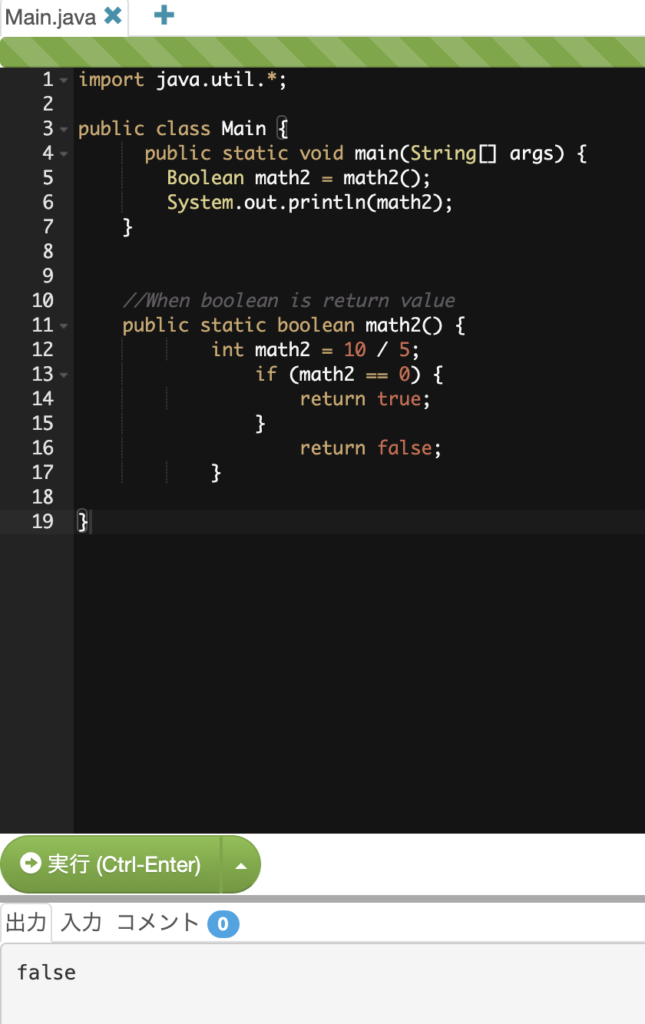
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boolean math2 = math2();
System.out.println(math2);
}
//When boolean is return value
public static boolean math2() {
int math2 = 10 / 5;
if (math2 == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}What does ”void” mean?
It's often shown as main function. What does void mean?
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
Void is used when there are no return value.
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}