Among the economic problems that Japan has, the problem of depopulation in rural areas has become one of the major issues.
As a result of the outflow of population from rural areas to urban areas and the further aging of people in rural areas, it is becoming more and more difficult to maintain villages.
In such a situation, Japanese government started the "Local Vitalization Cooperation" system in 2009, and started to solve the problem of depopulation in rural areas.
What is the current situation of depopulation in rural areas in Japan? And what kind of system is this "Local Vitalization Cooperation System"?
Depopulation problem in rural area of Japan.
The migration from rural areas to metropolitan areas has never stopped and continues to this day.
The graph below shows the excess number of people moving in and out of the metropolitan and regional areas.
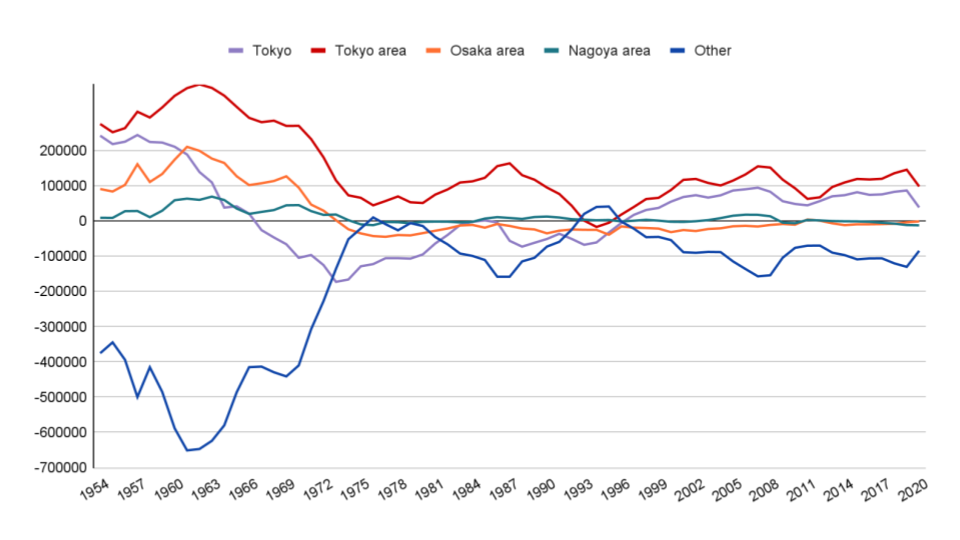
From 1954 to 1970, during Japan's period of rapid economic growth, there was a massive migration of people from rural areas to the Tokyo and Osaka metropolitan areas.
After that, there were basically 100,000 people moving in and out of the Tokyo metropolitan area and the rural areas every year.
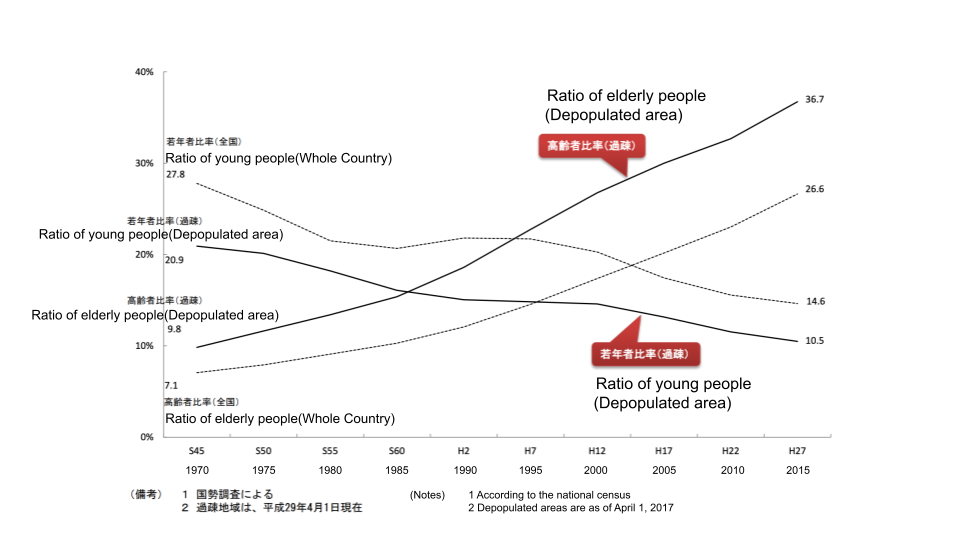
Depopulated areas and aging population
According to a survey by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, the number of marginalized villages exceeds 10,000, and more than 100 have disappeared. Depopulation is a serious situation.
Data from the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications also shows that the aging rate in depopulated areas is faster than in large cities.
Effects of Depopulation
What are the specific negative effects of depopulation? The following are some of the possible negative effects.
- Decrease in the number of job opportunities
- Increase in the amount of abandoned land
- Increase in the number of aging and vacant houses
- Problems such as animal damage and pest damage
- Decline in the standard of living of local residents due to the closure of local stores and supermarkets, and a decline in the convenience of public transportation
- Negative impact on urban life due to the disappearance of farmers in terms of food supply
- Loss of conservation of large areas of farmland and forests will have a negative impact on environmental sustainability and global warming countermeasures, including in urban areas.
As the number of depopulated areas increases, many negative effects will be felt not only in rural areas but also in large cities.
In order to solve these problems, Local Vitalization Cooperation system was established.
What is the Local Vitalization Cooperation system (地域おこし協力隊制度)?

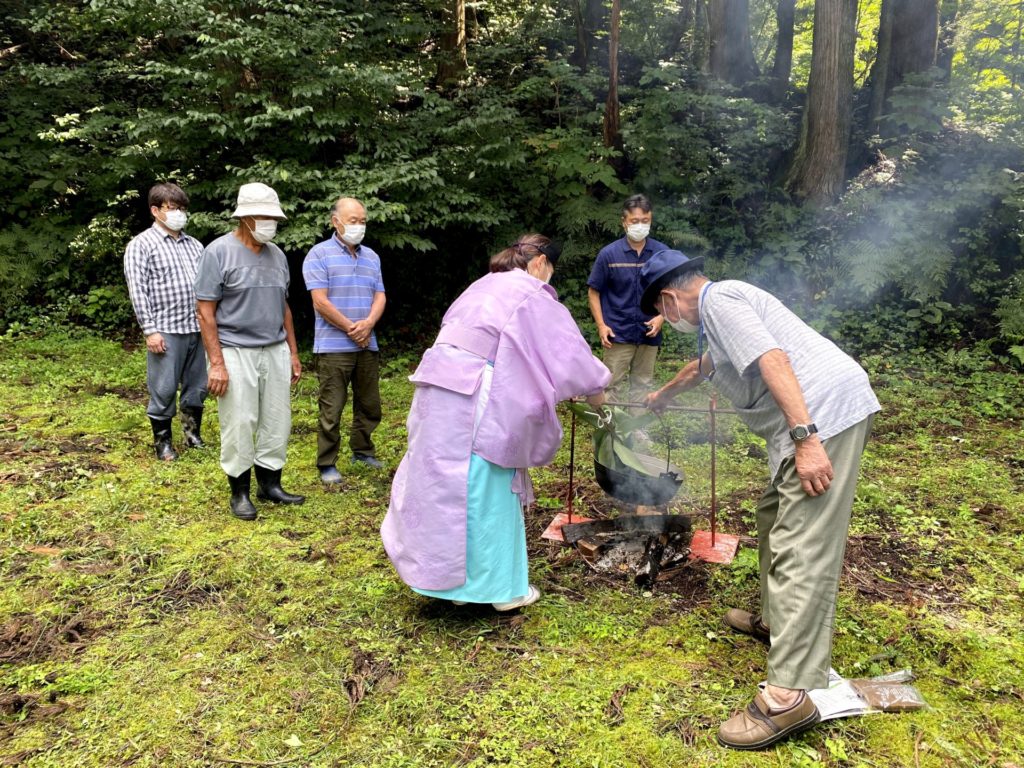
Local Vitalization Cooperation system is an initiative for people from urban areas to migrate to depopulated areas and settle down in those areas while cooperating regional activities.
The purpose of this program is to attract young people from urban areas to rural areas.
Regional activities cover a wide range of activities.
members are responsible for a variety of local activities, such as working in agriculture and fishery, which are the main industries of rural areas, promoting the attractions of the region, and organizing festivals and events. members work for the community rather than working for a company.
The term is one to three years, and the compensation is about 150,000 to 180,000 yen per month. Housing is often provided by the local community, and utility bills are generally paid by members. Salary for members is provided by the government.
In many cases, the employment status is part-time special position. Although cooperators become civil servants, they have a fixed term of office and are treated differently.
Advantages of Local Vitalization Cooperation
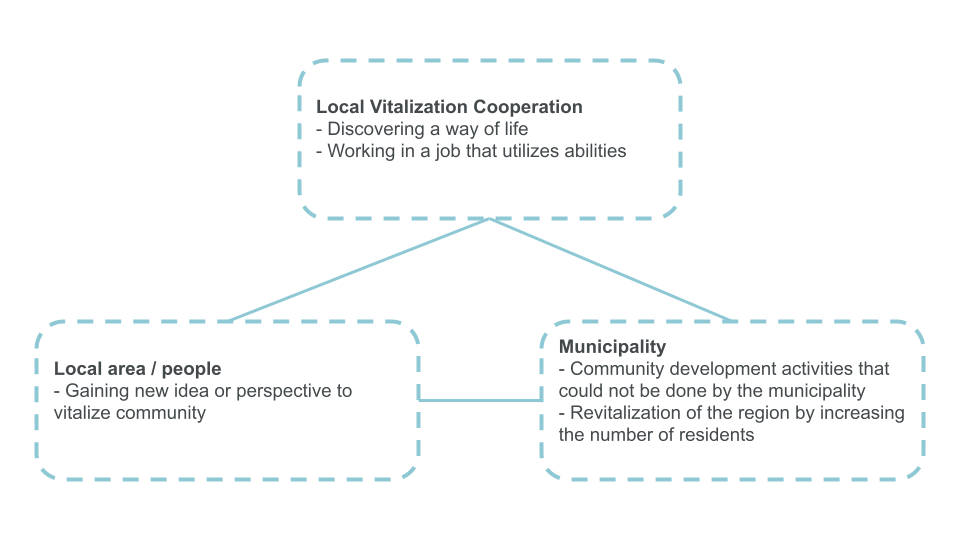
What are some of the benefits of Local Vitalization Cooperation?
Advantages for the municipality
Here's advantages for the municipality.
promoting the region from a new perspective.
People who have lived in the area for a long time may not be aware of its charms, but those who have moved to the area may easily notice them.
A life surrounded by nature may be normal for people from the countryside, but it may be new to those who have lived in the city.
It is easy to incorporate such attractions that are noticed from an outsider's point of view.
Attracting people with new skills
Applicants can incorporate the experience and skills they have developed in their careers to the local area.
municipalities have opportunities to cooperate with members who have IT skills, marketing, finance, and other business skills in the local area.
Advantages for the members
Here's advantages for the members:
members don't need to find job
What is different from ordinary immigration is that there is a job from the start. Usually people need to find jobs to migrate. But if people use this system, job is already prepared and applicants don't need to find job to migrate.
Place to live is secured
In many cases, the municipality that contracts with Local Vitalization Cooperation will provide a place to live, and the municipality will also pay the rent. So members don't need to rent house.
Locals are easy to understand why members are moved
In rural areas of Japan, a stranger moving in suddenly can be suspicious and it might be hard for migrants to get along with communities.
but if members are known to be a person brought in by the municipal office, it's easy for locals to understand why new people started to live with communities.
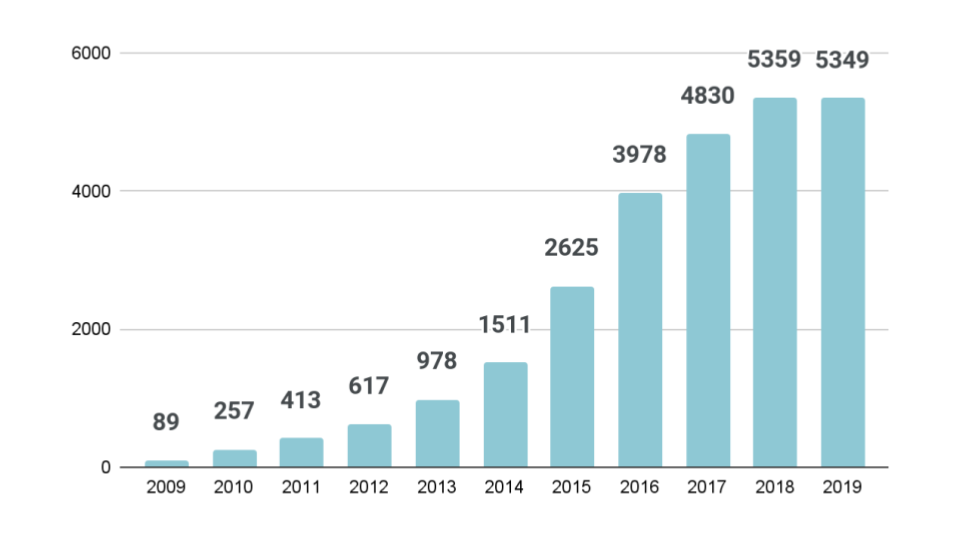
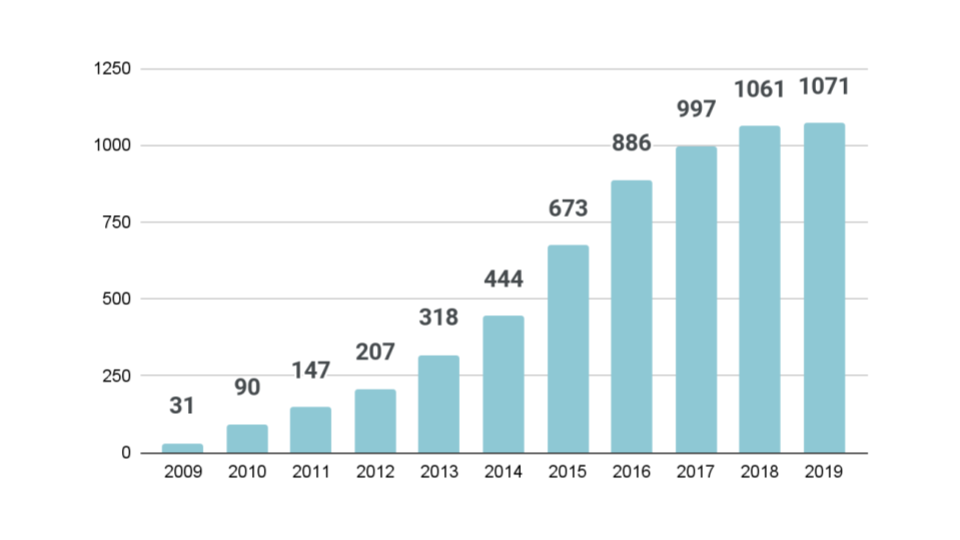
Number of Local Vitalization Cooperation
This system started in 2009. More than 5,000 people were active in 1,061 municipalities in 2018.
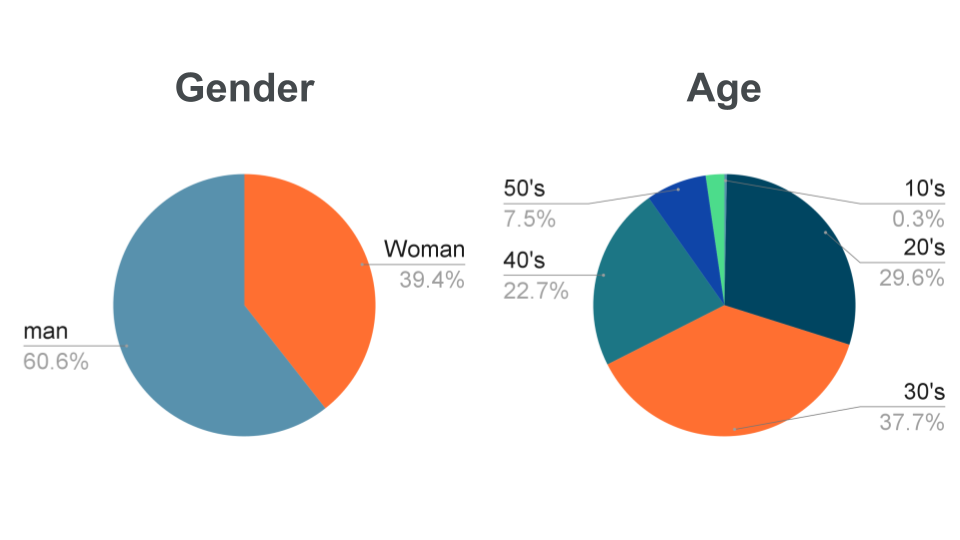
According to the 2019 data, the gender ratio was 60% male and 40% female, and 60% of the applicants were in their 20s and 30s.
Can non-Japanese participate in Local Vitalization Cooperation?
At the time of writing, Application page for Local Vitalization Cooperation for non-Japanese doesn't exist, but there are some areas that have added recruitment for foreigners as well.
For example, the qualifications for Tokushima Prefecture's 2021 application are as follows:
Applicants must meet all of the following requirements : 1. foreign nationals 2. have an understanding of and desire for regional development 3. Those who have the appropriate status of residence for the position they are applying for, or those who are able to change their status before being hired. 4. must be able to meet the regional requirements for the "Local Vitalization Cooperation" set forth by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (*1), such as changing one's certificate of residence after being hired in Japan. 5. Those who have completed the JET Programme or have the same level of ability as those who have completed the JET Programme (e.g., have obtained the status of residence "Education", "Technical/Humanities/International Services", or "Technical", or have passed the Japanese Language Proficiency Test N3 or higher), and are able to communicate in Japanese on a daily basis. 6. have the necessary qualifications and experience for each job (see the list of "Available Jobs") Regional requirements (*1) for the "Regional Development Cooperation Volunteers" means that a person who has a certificate of residence in an urban area in Japan moves his or her base of life to a depopulated area, mountain village, or remote island in Tokushima Prefecture and transfers his or her certificate of residence. In addition to moving from the three major metropolitan areas and designated cities in Japan, those who have completed the JET Program may also move to urban areas in Tokushima Prefecture. (Added on July 17, 2020)
Reference: 今さら人に聞けない、「地域おこし協力隊」って? 制度の意義から、着任までのステップ、メリット&デメリットまで 地域おこし協力隊とは 過疎化の現状と問題点とは? どんな対策ができるか Local Vitalization Cooperation website (Japanese)






